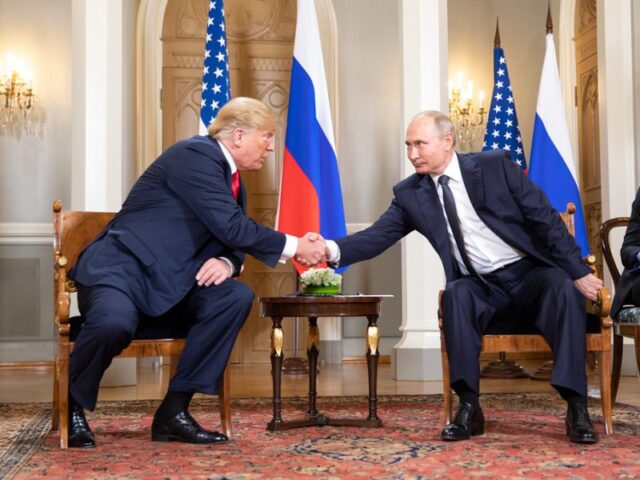
In a high-stakes diplomatic move, President Donald Trump and Russian President Vladimir Putin have reached a partial ceasefire agreement, focusing specifically on halting attacks on Ukraine’s energy infrastructure for the next 30 days. The agreement marks a significant but limited step in addressing the ongoing war in Ukraine, with major points of contention still unresolved.
Key Terms of the Agreement
The ceasefire agreement between Trump and Putin includes:
✅ A 30-day halt on strikes targeting Ukraine’s energy grid, including power plants, substations, and oil depots. This aims to prevent further blackouts and humanitarian crises as Ukraine battles harsh winter conditions.
❌ No agreement on a broader 30-day ceasefire, despite US and Ukrainian efforts to secure a temporary pause in hostilities. Putin refused to endorse a full ceasefire, maintaining that Ukraine must first stop receiving foreign military aid.
🔄 A planned exchange of 175 prisoners of war, expected to take place today. This marks one of the largest swaps between the two sides in recent months.
🌊 Future talks on a maritime ceasefire in the Black Sea, a vital trade route for both Ukraine and Russia. The negotiations could determine safe passage for grain exports and commercial shipping.
Ukraine’s Response
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy acknowledged the energy ceasefire as a positive step but firmly rejected Putin’s demand to halt foreign military aid. “Ukraine will not negotiate under pressure,” Zelenskyy stated, reaffirming his country’s reliance on Western support to counter Russian advances.
Western allies, including the United States and NATO members, have also dismissed Russia’s demand, calling it an unrealistic precondition that would leave Ukraine vulnerable.
Geopolitical Implications
The agreement reflects Trump’s diplomatic strategy of direct negotiations with world leaders, seeking limited but tangible gains rather than comprehensive peace deals. His willingness to engage Putin contrasts sharply with previous US administrations, which focused on supporting Ukraine militarily rather than negotiating directly with Moscow.
However, Putin’s refusal to expand the ceasefire beyond energy infrastructure suggests that Russia is not prepared to make major concessions. The Kremlin continues to push for conditions that weaken Ukraine’s defense capabilities, while using temporary agreements to ease international pressure.
Meanwhile, European leaders are discussing the possibility of deploying peacekeepers to monitor ceasefire violations and ensure stability, though such a move could escalate tensions with Russia.
What Comes Next?
✅ Monitoring of the ceasefire agreement to determine whether Russia abides by the 30-day pause on energy strikes.
✅ Execution of the prisoner exchange, which could serve as a trust-building measure for future negotiations.
✅ Further discussions on a potential Black Sea ceasefire, which could impact global food markets due to Ukraine’s key role in grain exports.
✅ Continued Western military aid to Ukraine, despite Russian objections.
Conclusion
While the partial ceasefire offers temporary relief, it is far from a lasting solution to the war. With Putin standing firm on territorial demands and Ukraine refusing to compromise on military support, the path to broader peace remains uncertain. The coming weeks will reveal whether this limited agreement paves the way for further negotiations—or simply serves as another short-term truce in a prolonged conflict.