The Critical Role of Sleep in Brain Function
Sleep is essential for maintaining cognitive health and overall brain function. Recent research has revealed that disrupted or inadequate sleep significantly hampers the brain’s glymphatic system, the specialized network responsible for clearing out waste and toxins. Without proper rest, harmful proteins accumulate, increasing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases and memory decline.
Understanding the Glymphatic System
The glymphatic system is the brain’s unique waste disposal network, functioning similarly to the lymphatic system in the rest of the body. It is most active during deep sleep, utilizing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to flush out metabolic waste, including beta-amyloid and tau proteins, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. When sleep is disrupted, this process is impaired, leading to toxin buildup and increased susceptibility to cognitive decline.
The Consequences of Poor Sleep
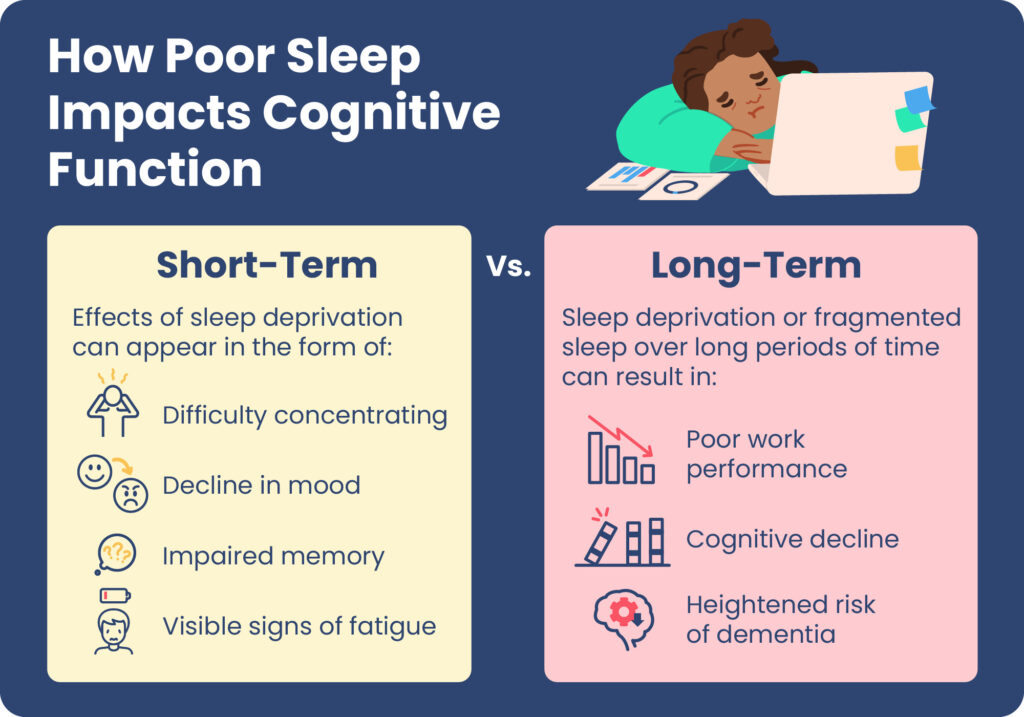
1. Increased Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Studies indicate that inadequate sleep heightens the risk of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative conditions. The accumulation of toxic proteins accelerates neuronal damage, ultimately affecting memory, decision-making, and cognitive function.
2. Memory Decline and Cognitive Impairment
Deep sleep is crucial for memory consolidation. Poor sleep reduces the brain’s ability to process and store information effectively, leading to forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, and slower cognitive performance.
3. Mental Health Challenges
Sleep deprivation is linked to increased levels of stress, anxiety, and depression. Chronic sleep disturbances can exacerbate mood disorders and hinder emotional regulation.
The Impact of Sleeping Pills on Brain Cleaning Mechanisms
While some individuals turn to sleep aids like zolpidem to combat insomnia, recent studies highlight potential drawbacks. A functional MRI study of 72 participants revealed that zolpidem reduced the brain’s natural cleaning mechanisms by 50%, further hindering the glymphatic system’s ability to remove toxins. Over time, dependence on sleep medications may do more harm than good, potentially increasing the risk of neurological disorders.
How to Improve Sleep and Support Brain Health
To optimize brain function and maintain cognitive health, consider implementing the following sleep hygiene practices:
- Prioritize Deep Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to ensure the glymphatic system functions properly.
- Follow a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate the body’s internal clock.
- Create a Restful Environment: Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool to promote uninterrupted sleep.
- Limit Blue Light Exposure: Reduce screen time before bed to prevent disruptions in melatonin production.
- Avoid Sleeping Pills When Possible: Opt for natural sleep aids like magnesium, chamomile tea, or mindfulness meditation instead of relying on medication.
- Stay Physically Active: Regular exercise improves sleep quality and overall brain function.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, or journaling to reduce anxiety-induced sleep disturbances.
Conclusion
The connection between sleep and brain health is undeniable. Poor rest disrupts the glymphatic system, leading to harmful toxin buildup and increasing the risk of neurological diseases. Additionally, reliance on sleeping pills may further impair the brain’s natural cleansing process. Prioritizing sleep hygiene and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help protect cognitive function, ensuring long-term mental well-being.