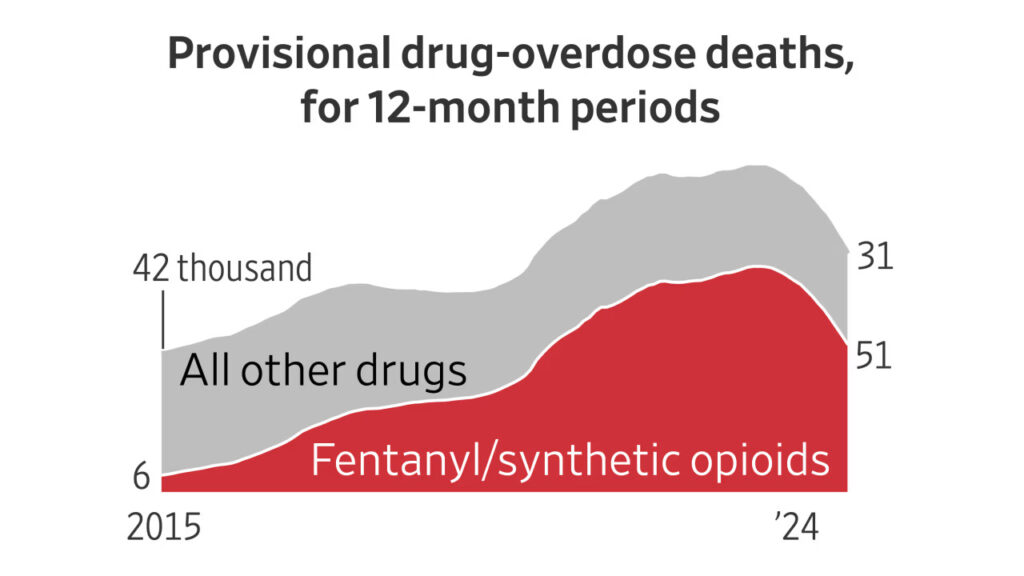
The United States has witnessed a significant decline in drug overdose deaths, marking a potential turning point in the ongoing opioid crisis. According to recent data, from October 2023 to October 2024, drug overdose fatalities dropped by 24%, with approximately 87,000 deaths recorded—a stark improvement from previous years. This decline equates to an estimated 70 lives saved each day.
Key Factors Driving the Decline
1. Decrease in Synthetic Opioid Fatalities
One of the most notable shifts is the reduced number of deaths involving synthetic opioids, particularly fentanyl. While fentanyl has been a major contributor to overdose deaths in the past decade, efforts to curb its impact are showing promising results. Increased public awareness, targeted law enforcement actions, and advancements in substance monitoring have contributed to this downward trend.
2. Expanded Access to Naloxone
The widespread distribution of naloxone, a life-saving overdose reversal drug, has played a crucial role in reducing fatalities. Federal and state initiatives have made naloxone more accessible to first responders, community organizations, and even individuals at risk of overdose. By quickly reversing the effects of opioid overdoses, naloxone has saved thousands of lives across the country.
3. Improved Treatment Availability
Access to effective treatment options such as methadone and buprenorphine has significantly improved. These medications, part of Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT), help individuals struggling with opioid addiction by reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Increased federal funding and policy changes have expanded access to these treatments, particularly in underserved areas.
4. Shifts in Drug Supply and Usage Trends
Analysts have observed changes in the illicit drug market, with some users opting for less potent substances. This shift may be due to increased education on the dangers of fentanyl-laced drugs, as well as efforts to regulate and intercept illicit drug supplies before they reach communities.
Regional Impact and Nationwide Trends
Data indicates that 45 states reported a reduction in overdose deaths, highlighting the effectiveness of nationwide efforts to combat the crisis. However, despite this positive trend, drug overdose remains the leading cause of death for Americans aged 18 to 44. This underscores the importance of continued investment in prevention, treatment, and harm reduction strategies.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While the recent decline in overdose deaths is encouraging, experts caution that sustained efforts are necessary to maintain and further this progress. Challenges remain, including the emergence of new synthetic drugs, barriers to treatment access in rural areas, and the need for ongoing education and prevention programs.
The Biden administration, public health agencies, and community organizations continue to push for long-term solutions, focusing on a comprehensive approach that includes stricter regulations on illicit drug distribution, enhanced mental health support, and expanded harm reduction strategies.
Conclusion
The 24% drop in US drug overdose deaths marks a hopeful shift in the fight against the opioid epidemic. With continued efforts in harm reduction, treatment accessibility, and public awareness, the nation may be on the path to a sustained decline in overdose fatalities. However, ongoing vigilance and proactive policies will be essential to ensure that these gains are not temporary, but rather a lasting step toward overcoming the crisis.