The U.S. economy saw notable shifts in January as producer prices increased while jobless claims declined, reflecting continued economic activity and labor market resilience.
Producer Prices Increase
The Producer Price Index (PPI), which measures the prices that businesses receive for their goods and services, rose by 0.4% in January. This followed a revised 0.5% increase in December, indicating persistent price pressures in the supply chain. On a year-over-year basis, producer prices were up by 3.5%, highlighting ongoing inflationary trends.
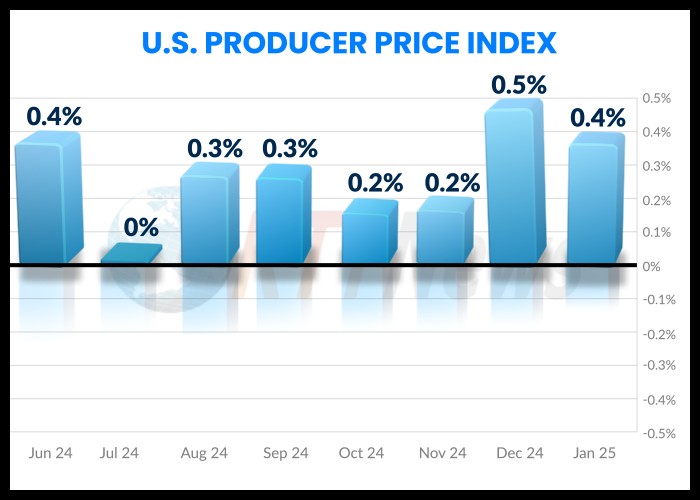
Wholesale goods prices experienced a 0.6% uptick, primarily driven by a 1.7% increase in energy costs. The energy sector’s rising costs had a cascading effect on various industries, contributing to the overall increase in producer prices. Food prices also surged by 1.1%, with egg prices seeing a particularly sharp rise of 44%, largely due to an avian flu outbreak that led to a significant reduction in poultry supply.
Meanwhile, service-related costs climbed 0.3%, reflecting higher consumer demand and operational expenses. Notably, hotel room prices spiked by 5.7%, driven by increased travel activity and seasonal factors.
Jobless Claims Decline
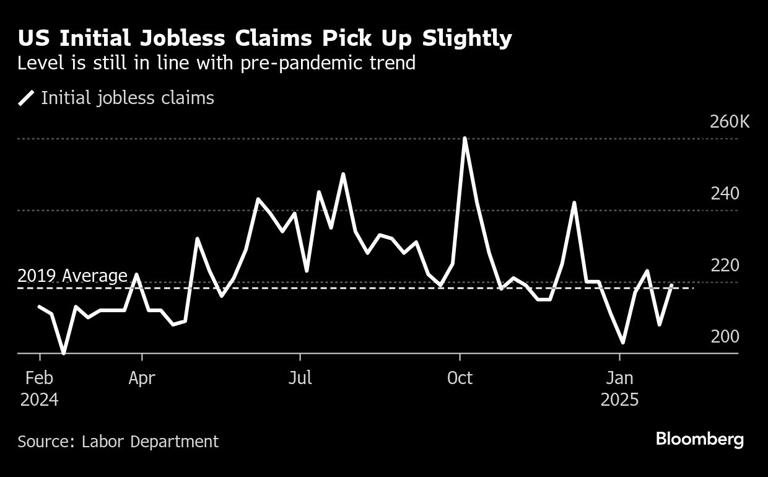
Despite rising producer prices, the labor market displayed resilience, as initial jobless claims dropped by 7,000 to 213,000 in January. This decline suggests a stable employment environment, with fewer individuals filing for unemployment benefits. Continuing jobless claims also fell by 36,000 to 1.85 million, indicating that more workers are securing employment or exiting the unemployment system.
Nonfarm payrolls added 143,000 jobs in January, reflecting steady hiring across various industries. The unemployment rate remained at 4.0%, signaling a balanced labor market where job opportunities continue to be available, despite broader economic concerns.
Economic Outlook
The increase in producer prices suggests that inflationary pressures remain a challenge for businesses and consumers alike. Higher input costs could lead to increased consumer prices, potentially influencing Federal Reserve policy decisions regarding interest rates.
However, the decline in jobless claims and steady employment growth indicate economic resilience. If labor market stability continues, consumer spending may remain strong, helping sustain economic momentum despite inflationary pressures.
As the Federal Reserve monitors these economic indicators, future policy decisions will likely focus on balancing inflation control with labor market health. The coming months will be crucial in determining whether producer price increases stabilize and how the labor market responds to evolving economic conditions.